Structure-Revealing Low-Light Image Enhancement via Robust Retinex Model
Abstract
Low-light image enhancement methods based on classic Retinex model attempt to manipulate the estimated illumination and project it back to the corresponding reflectance. However, the model does not consider the noise, which inevitably exists in images captured in low-light conditions. In this paper, we propose the robust Retinex model, which additionally considers a noise map compared with the conventional Retinex model, to improve the performance of enhancing low-light images accompanied by intensive noise. Based on the robust Retinex model, we present an optimization function that includes novel regularization terms for the illumination and reflectance. Specifically, we use l1 norm to constrain the piece-wise smoothness of the illumination, adopt a fidelity term for gradients of the reflectance to reveal the structure details in low-light images, and make the first attempt to estimate a noise map out of the robust Retinex model. To effectively solve the optimization problem, we provide an augmented Lagrange multiplier based alternating direction minimization algorithm without logarithmic transformation. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in low-light image enhancement. In addition, the proposed method can be generalized to handle a series of similar problems, such as image enhancement for underwater or remote sensing, and in hazy or dusty conditions.
Citation
@article{li2018structure, title={Structure-Revealing Low-Light Image Enhancement via Robust Retinex Model}, author={Li, Mading and Liu, Jiaying and Yang, Wenhan and Sun, Xiaoyan and Guo, Zongming}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Image Processing}, volume={27}, number={6}, pages={2828-2841}, month={June}, year={2018}, }
Selected Results
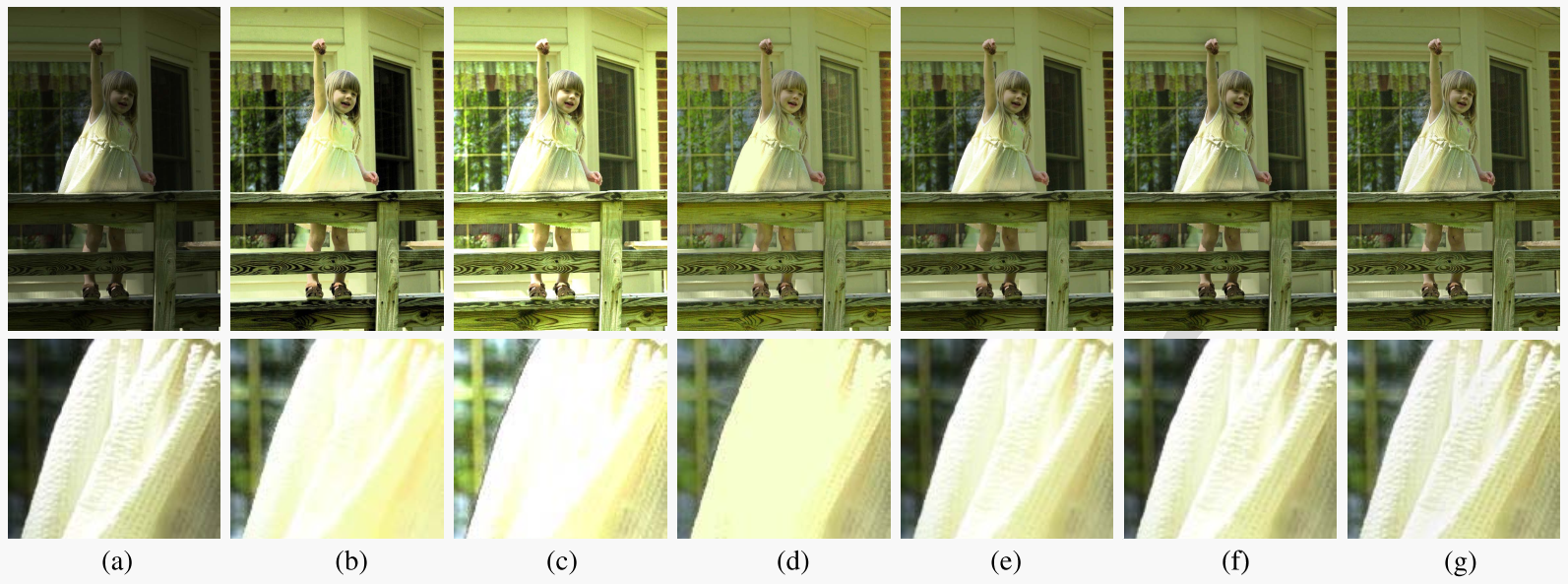

Fig. 1. Comparisons of low-light image enhancement results. From left to right, they are the input images, results generated by HE, LIME [1], NPE [2], PIE [3], SRIE [4], and the proposed method.
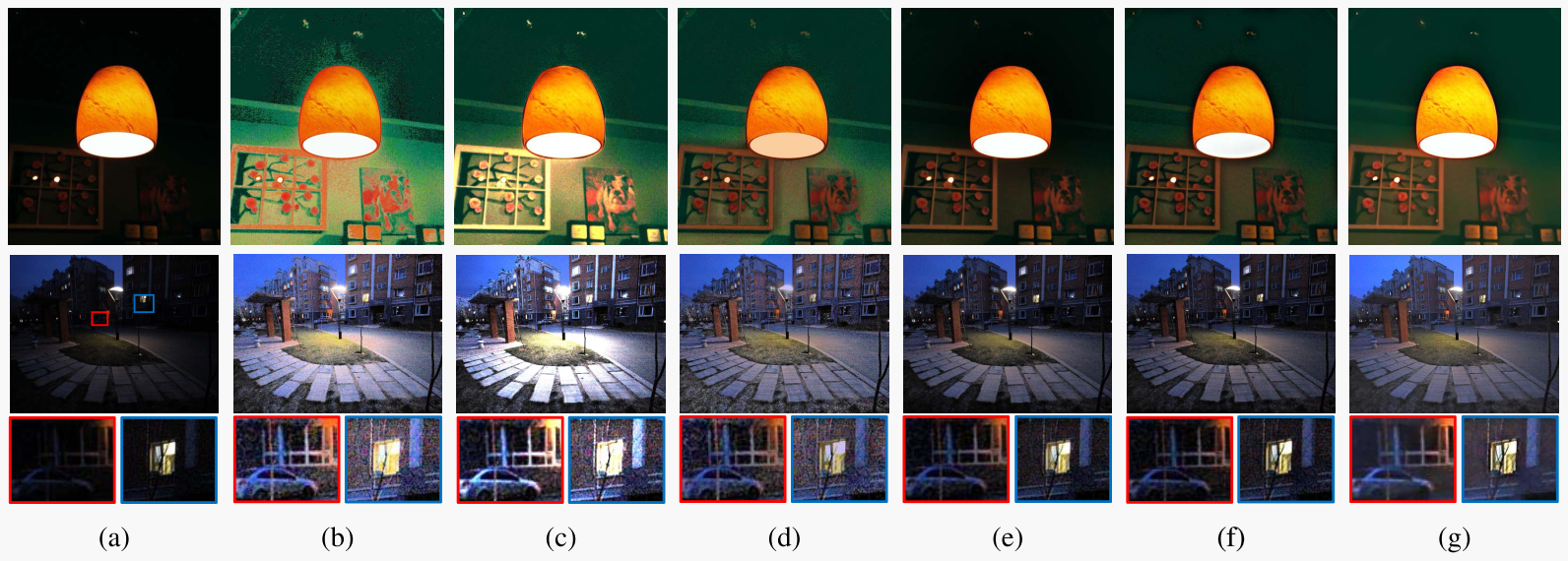
Fig. 2. Comparison of simultaneously low-light enhancement and noise suppression. For each case, from left to right, they are the input images, results generated by HE, LIME [1], NPE [2], PIE [3], SRIE [4], and the proposed method.
Reference
[1] X. Guo, Y. Li, and H. Ling, LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation, TIP 2017.[2] S. Wang, J. Zheng, H.-M. Hu, and B. Li, Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images, TIP 2013.
[3] X. Fu, Y. Liao, D. Zeng, Y. Huang, X. P. Zhang, and X. Ding, A probabilistic method for image enhancement with simultaneous illumination and reflectance estimation, TIP 2015.
[4] X. Fu, D. Zeng, Y. Huang, X. P. Zhang, and X. Ding, A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation,
[4]CVPR 2016.